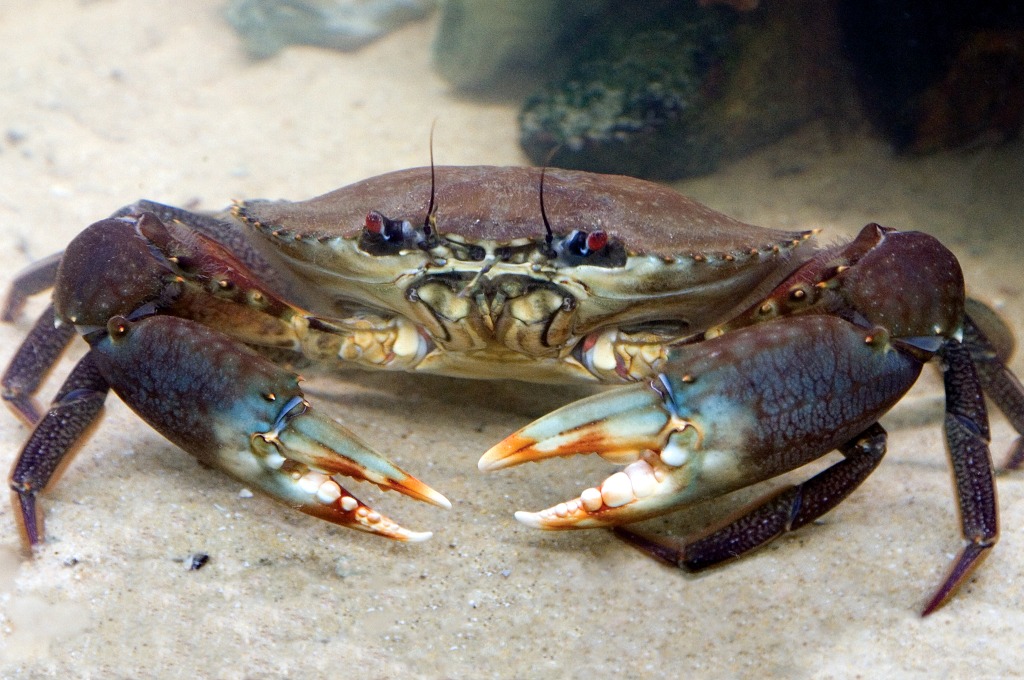
Prized by recreational fishers for their impressive size and delicious taste, green mud crabs are targeted by fishers throughout tropical Australia.
Scientific name
Scylla serrata
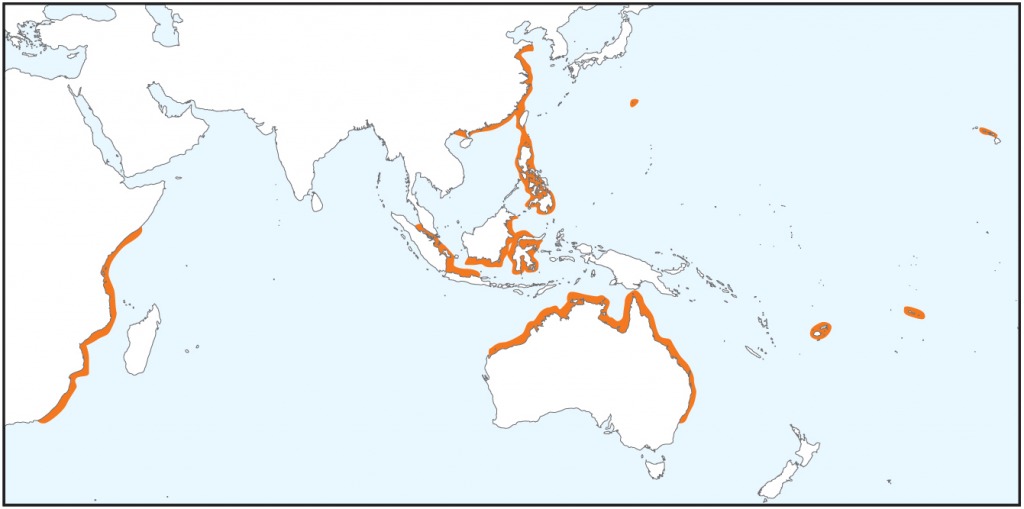
Distribution
From East and South Africa to Southeast and East Asia (from Sri Lanka and SE of China), and Northern Australia (Bega River, NSW to Exmouth Gulf). Also found around the Marianas, Fiji and Samoan Islands. Introduced in the Hawaiian Archipelago.
In Australia, Shark Bay to the Northern Territory border.
Ecological suite
Crustaceans
General description
Prized by recreational fishers for their impressive size and delicious taste, green mud crabs are targeted by fishers throughout tropical Australia. Emerging from their burrows at night to forage for food; they eat almost anything.
Fast and strong, their claws can be extremely dangerous. Mud crabs use their claws to defend themselves and will even shed a claw to escape. In many cases, a new, fully functional claw will grow back. To the unsuspecting fisher, once a crab has locked on, its claw will remain in a vice like grip even if detached from its body.
Whilst known as a tropical species, they are highly tolerant of variations in water salinity and temperature. When the Leeuwin Current flows strongly, short-lived populations of green mud crabs can be found as far south as Wilson Inlet near Denmark.
The cooked flesh is moist, flaky and sweet, and for many, considered the best eating crustacean.
Other names
Giant mud crab, mangrove crab, black crab, muddy
Habitat
Prefers the more saline waters of estuary and mangrove areas, requiring soft, muddy bottoms to dig deep burrows. Although many occupy burrows in the intertidal zone, most adults live in areas that are below the low tide mark.
Colour
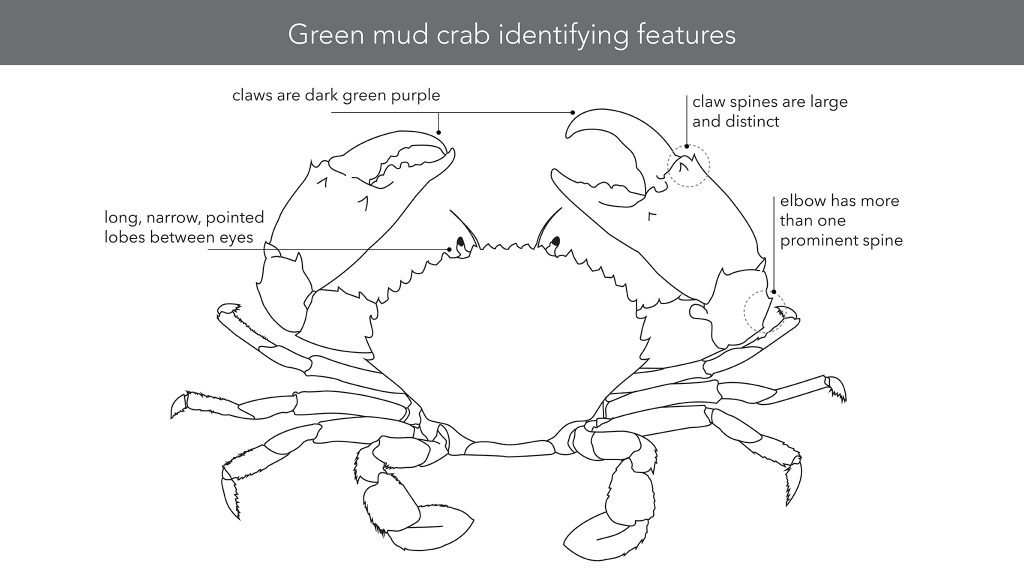
Very dark brown to mottled green with claws dark green purple. Obviously patterned (mottled) walking legs.
Size
Grows to 30 cm carapace width.
Diet
Molluscs, smaller crabs, worms and plant material
Exploitation
The commercial mud crab fishery is relatively small in Western Australia, producing between 5-10 tonnes annually. The recreational fishery for mud crab is also significant, with mud crabs being a highly targeted species.
Safety
Handle with care.