Seen from space, it is no wonder that planet Earth is referred to as the 'Blue Planet'.
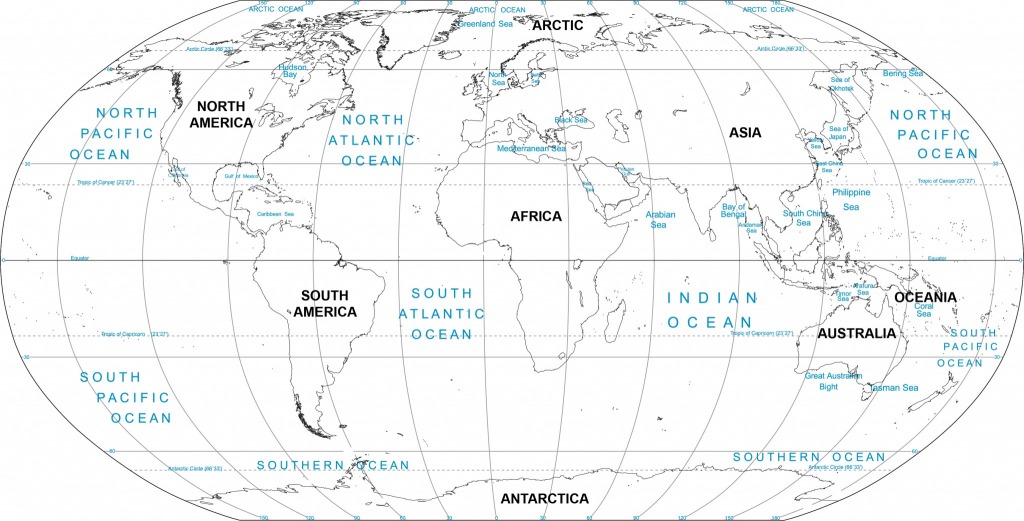
Oceans occupy 71 percent of the world’s surface. Although oceans are all interconnected, five bodies of seawater are designated as oceans.
| Surface Area (million km2) | Volume (million km3) | |
| Pacific Ocean | 153 | 644 |
| Atlantic Ocean | 82 | 308 |
| Indian Ocean | 67 | 262 |
| Southern Ocean | 21 | 72 |
| Arctic Ocean | 9 | 4 |
Table 1. Surface area and volume of the world’s five oceans.
All the oceans, except the Southern Ocean, occupy hollows on the earth’s surface called basins.
The Southern Ocean boundary was established at the 60°S latitude in 2000 by the International Hydrographic Organisation and coincides with the area under jurisdiction of the Antarctic Treaty of 1959.
A cover of ice distinguishes the Arctic Ocean. The division of this ocean is somewhat complex and lies almost entirely above the Arctic Circle.
Smaller areas of the ocean are referred to as seas, gulfs and bays. These areas have unique characteristics that are generally distinct from those of the ocean to which they are connected to.
The naming of these areas is somewhat subjective. The definitions loosely are as follows:
Seas – an area that is part of an ocean, or is partially or fully enclosed, e.g. Timor Sea.
Gulf – an area of ocean forming a coastal indentation often larger than a bay, e.g. Exmouth Gulf.
Bay – an area of ocean surrounded by land on three sides, e.g. Geographe Bay.
Bight – an area of ocean similar to a bay, but with a very wide opening to the ocean, e.g. Great Australian Bight.
References:
Castro, P. and Huber, M.E. 2003, Marine Biology, 4th Ed, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), World Fact Book, https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/
Crist, D.T., Scowcroft, G. and Harding, J.M. 2009, World ocean census: a global survey of marine life, Firefly Books, New York.
International Hydrographic Organisation, https://iho.int/
Vocabulary
Bay
An area of ocean surrounded by land on three side, e.g. Geographe Bay.
Bight
An area of ocean similar to a bay, but with a very wide opening to the ocean, e.g. Great Australian Bight
Continent
Large land masses of Earth, regarded as including Africa, Antarctica, Asia, Australia, Europe, North America and South America.
Equator
An imaginary line around the earth equidistant from the poles, dividing the Earth into two equal symmetrical parts, i.e. Northern and Southern hemispheres.
Ocean
Continuous body of saltwater covering the majority of the earth’s surface, geographically divided into the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern and Arctic Oceans.
Seas
An area that is part of an ocean, or is partially or fully enclosed, e.g. Timor Sea.